The efficiency of public spending in India comes in for criticism, as does the expansion of contract teaching jobs in public schools.
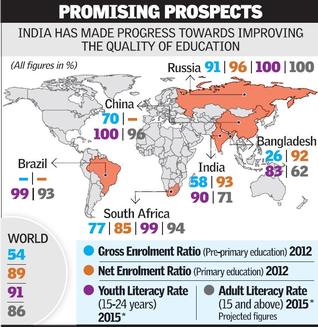
India has made remarkable strides towards ensuring education for all, a new global monitoring report shows. While access is now close to universal, the quality of education remains a major challenge, it says.
In April 2000, the governments of 164 countries adopted the Dakar Framework to deliver Education For All commitments by 2015. On Thursday, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO) published the Education For All Global Monitoring Report to evaluate the progress of countries on these goals.
India is likely to reach the EFA’s first goal of 80 per cent enrolment in pre-primary education by 2015, has already reached the second goal of universal primary enrolment, and will fall just short of universal youth literacy by 2015, the report said. The one measurable goal India will not reach is to reduce its adult illiteracy rate by half (it has reduced it by 26 per cent). The country’s major success has been in reaching gender parity for primary and lower secondary enrolment, the only country in South and West Asia to do so. It has also made progress towards improving the quality of education, but major gaps remain.
According to the report, nearly half of all countries have achieved universal pre-primary, primary and lower secondary enrolment. Only 25 per cent of the countries have reduced by half their levels of adult illiteracy, and women continue to make up two-thirds of the illiterate. Two-thirds of the countries have also achieved gender parity at the primary level, but less than half at the secondary level.
“Overall, not even the target of universal primary education was reached, let alone the more ambitious EFA goals, and the most disadvantaged continue to be the last to benefit. But there have been achievements that should not be underestimated. The world has advanced by 2015 beyond where it would have been if the trends of the 1990s had persisted,” the report says. “A lesson re-emerging over the past 15 years is that while technical solutions are important, gaining political influence and traction is of even greater significance,” it notes.
However, major challenges remain. The efficiency of public spending in India comes in for criticism, as does the expansion of contract teaching jobs in public schools.
Most crucially, the “Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) said that while India’s education system succeeded in enrolling many more children, there were wide disparities in students’ achievement of basic skills across the States, a finding validated in the official National Achievement Survey of grade 3 students,” the report says.Hindu
Picture Source :